In today’s increasingly digitized and interconnected world, financial institutions are under constant pressure to prevent fraud, ensure compliance, and promote transparency. Three foundational pillars that guide these efforts are KYC (Know Your Customer), AML (Anti-Money Laundering), and CFT (Combating the Financing of Terrorism). Together, they form the backbone of modern-day banking compliance frameworks.
🔢 What is KYC?
Know Your Customer (KYC) refers to the process through which banks and financial institutions verify the identity of their customers before and during the course of a business relationship. It is a crucial component in risk management and fraud prevention.
Key Objectives of KYC:
- Verify the identity of customers and beneficial owners
- Understand the nature and purpose of customer relationships
- Assess risk profiles to apply appropriate due diligence
- Prevent identity theft and financial fraud
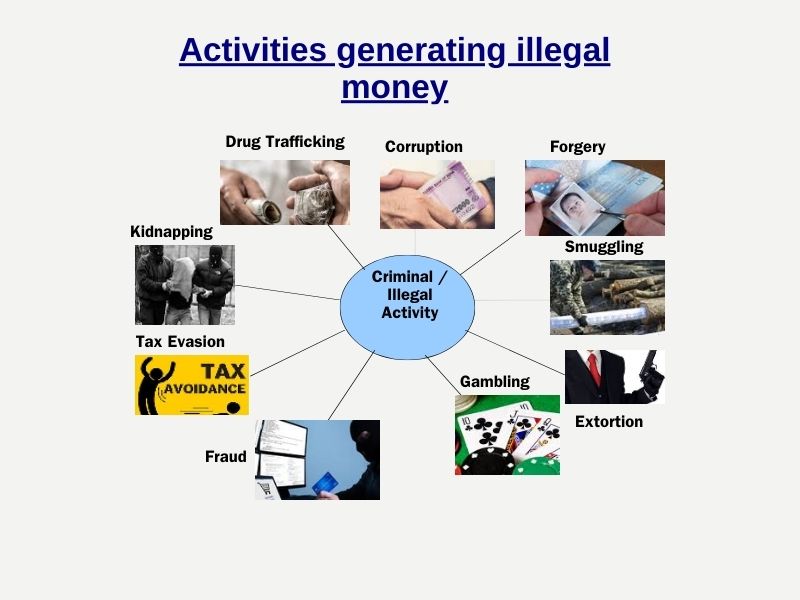
- The objective of KYC/AML/CFT guidelines is to prevent banks from being used, intentionally or unintentionally, by criminal elements for money laundering, terrorist financing and fraud.
- It reduces reputational, regulatory and legal risk.
🔎 Core Components of KYC:

- Customer Identification Procedure (CIP): Establishing identity through PAN, Aadhaar, Passport, etc.
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD): Verifying the authenticity of identity documents and assessing risk.
- Risk Categorisation : •Classifying Customers into ‘low’, ‘medium’ and ‘high’ risk categories depending on their AML risk assessment.
- Ongoing Due Diligence: Monitoring transactions to ensure consistency with the customer’s profile.
🧰 What is AML?

Money laundering is the process of creating an appearance that large amounts of dirty money obtained from such illegal sources into clean assets/ money.
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) is a broader regulatory framework designed to detect, report, and prevent activities related to illegal money.
Common Money Laundering Methods:
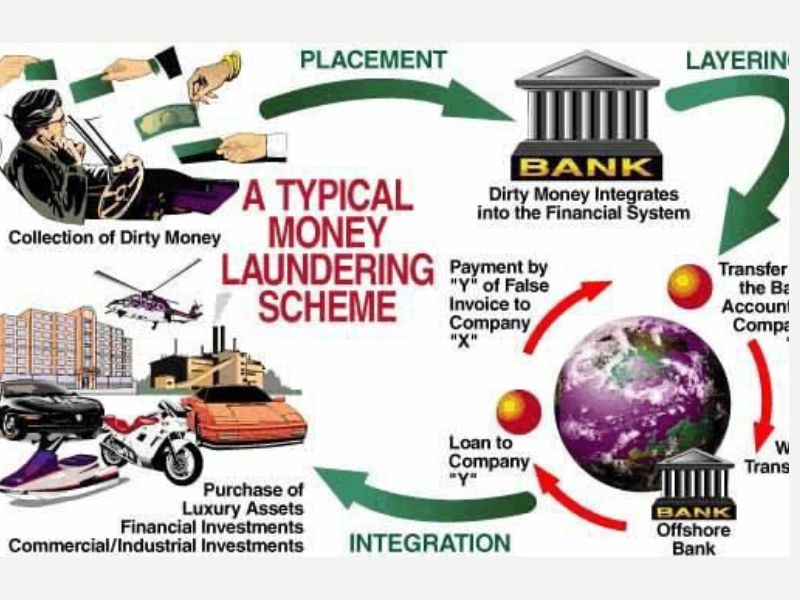
- Placement-Structuring or “smurfing” (breaking large sums into smaller deposits)
- Layering through multiple accounts and jurisdictions
- Use of shell companies
- Integration into formal Financial System
AML Measures Include:
- Suspicious Transaction Reports (STRs)
- Currency Transaction Reports (CTRs)
- Non-Profit-Organisation Transaction Reports (NTRs)
- Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) for high-risk clients
🚨 What is CFT?
Combating the Financing of Terrorism (CFT) is focused on identifying and curbing the financial channels that fund terrorist activities. CFT compliance ensures that funds are not misused for unlawful purposes.
How Banks Contribute to CFT:
- Flagging unusual cross-border transactions
- Blocking accounts linked to sanctioned entities
- Complying with the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) mandates
✅ Importance of KYC, AML & CFT for Banks
- 🌐 Global Compliance: Aligning with FATF, RBI, and FIU-IND norms
- ⚡ Risk Mitigation: Minimizing exposure to operational and reputational risk
- 🏦 Customer Trust: Reinforcing secure banking experiences
- ✉️ Regulatory Penalties: Avoiding heavy fines and sanctions
💡 KYC-AML-CFT Compliance Workflow:
- Customer applies to open an account
- Bank performs CIP and verifies KYC documents. Web checking should be done to verify genuineness.
- Risk category is assigned (Low/Medium/High)
- Periodic review and transaction monitoring begins
- STR/CTR/NTR is filed if suspicious behavior is detected
🔗 Role of Technology in Compliance
- AI and Machine Learning: Detecting transaction anomalies
- Biometric Verification: Strengthening identity checks
- Blockchain Audits: Ensuring transparency in transaction trails
⚠️ Common Challenges Faced:
- Lack of updated customer information
- Manual error in risk profiling
- Delayed STR reporting due to low awareness
🎯 Best Practices for Bank Staff
- Adhere to KYC checklists without exceptions
- Raise alerts on red-flagged transactions
- Update customer profiles periodically
- Maintain audit trails and training records
📅 Recent Regulatory Updates :
- FATF(Financial Action Task Force) established by G-7 in 1989 to combat money laundering and terrorism financing-Responsibility for developing global policy standards on AML & CFT
- August 2002- PREVENTION OF MONEY-LAUNDERING ACT(PMLA), 2002 passed & Guidelines of RBI on KYC issued-Master Directions on KYC
- November 2004- FIU-IND set up & Detailed guidelines on KYC
- January 2005- THE PREVENTION OF MONEY-LAUNDERING (MAINTENANCE OF RECORDS) RULES, 2005 framed & Implementation starts
- AADHAAR (TARGETED DELIVERY OF FINANCIAL AND OTHER SUBSIDIES, BENEFITS AND SERVICES) ACT, 2016.
- RBI 2023 KYC Master Direction Updates: Inclusion of Video KYC (V-CIP) norms
- FIU-IND Emphasis on prompt STR filing and training
- Aadhaar guidelines for offline and online use clarified
🎓 Learn More With Us
At Bharatiya Bank Coaching Centre, we offer practical, compliance-driven training on various topics on General Banking, Credit, NPA Management, Customer Service, Behavioral Science etc., helping banking professionals master different dimensions of modern banking.
Join our lessons to strengthen your understanding and stay compliant!

